Explain the Different Kinds of Measures of Dispersion
Deviation from the median. The dispersion of a statistical distribution is the measure of deviation of its values about the their average central value.
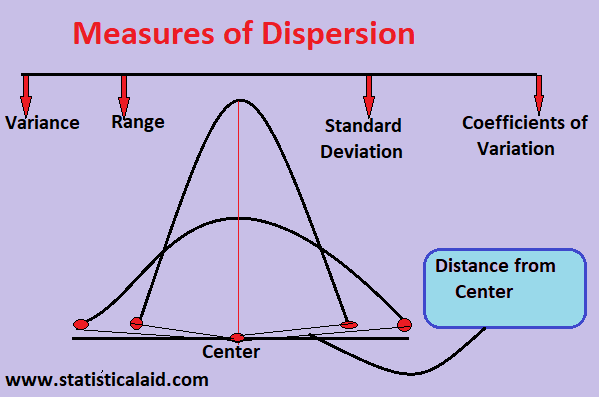
Measures Of Dispersion In Statistics And Its Types Statistical Aid
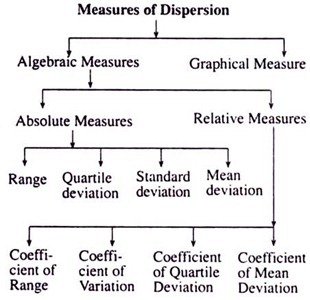
Absolute measures of dispersion Relative measures of dispersion.
. When mean is same for two data set the greater the spread the greater standard deviation. These measures give us an idea about the amount of dispersion in a set of observations. Absolute measures of dispersion indicate the amount of variation in a set of values.
Types of Relative Measures of Dispersion. Range is a measure of variability or scatteredness of. The range is the difference.
It is simply the difference between the maximum value and the minimum value given in a data set. This averaged deviation or dispersion is nothing else but the average of the second order. Coefficient of Mean deviation.
Q3 Q1 2 Q3 Q1. Most common measures of statistical dispersion are. Range mean deviation quartile deviation standard deviation and variance are examples of statistical dispersion measurements.
The standard deviation is regarded as a very good measure of series dispersion because it is a measure of. The range gives an overall picture of how widely spread the data is. It has a special utility in measuring variation in open end.
Variance is the most precise measure of how dispersed your data. Interquartile range which is a measure of the range within only the middle 50 of the data set. Q3 Q1 coefficient of QD.
Up to 8 cash back When it comes to measures of dispersion there are three concepts that give you an idea of how dispersed your data is. Relative measures of dispersion. In statistics dispersion is the degree to which a distribution is stretched or squeezed.
Range is the interval between the highest and the lowest score. Absolute measure of dispersion. Absolute Measures of Dispersion.
Dispersion in simple words means scattered or spread. It gives an idea of scatteredness of the different values from the average value. Different Measures of Dispersion are 1.
The taller-looking distribution shows a smaller dispersion while the wider distribution shows a larger dispersion. The types of absolute measures of dispersion are. Range refers to the difference between each series minimum and maximum values.
Absolute measures of dispersion. Characteristics of Measures of Dispersion. Standard deviation is used to measure spread or dispersion around the mean of data set.
There are four commonly used measures to indicate the variability or dispersion within a set of measures. Coefficient of Quartile Deviation. The following are examples of dispersion measures.
If we have two sets of observations we cannot always use. Generally these measures of dispersion are commonly used. There are two kinds of measures of dispersion namely.
Standard deviation gives an idea of how close together the data is compared to the mean. The dispersion is constantly dependent on the observations and types of central tendency metrics used. Absolute and Relative Measures of Dispersion Difference.
Deviation from the mean. If the dispersion is not known a mean value can be misleading. Relative measure of dispersion.
It is calculated by using the formula - QD. Deviation from the mean. In terms of units of observations.
It should be easy to. A measure of dispersion should be strictly defined. Measures of Dispersion.
You may notice that all the relative. Absolute measure of dispersion indicates the amount of variation in a set of values in terms of units of observations. What is different between the two is the spread or dispersion of the scores.
There are two types of measures of dispersion. Measures of dispersion are called averages of the second order because in precise study of dispersion the deviations of the size of items from a measure of central tendency are calculated ignoring the signs and then these deviations are averaged. 7 rows Measures of dispersion can be classified into two types ie absolute and relative.
RANGE The range is the difference between the. You can see both are normally distributed unimodal symmetrical and the mean median and mode for both fall on the same point. The measure of dispersion is the measure of the spread of scores in a data set.
There are four relative measures of dispersion. It includes range standard deviation quartile deviation etc. Range interquartile range and standard deviation are the three commonly used measures of dispersion.
There are two kinds of measures of dispersion namely. They give the answers in the same units as the units of the original observations. It is easy to calculate and.
It is the extent to which the values vary around the central or average value. 1 35 6 7 Range 7 -1 6. Relative measures of dispersion are free from the units of measurements of the observations.
Ad Over 27000 video lessons and other resources youre guaranteed to find what you need. Quartile deviation is an absolute measure of dispersion. Measures of Dispersion differs with location or central tendency and together they are one of the most used properties of distributions.
When the observations are in kilograms the absolute measure is also in kilograms. Standard deviation is never negative. Standard deviation which is a statistical measure used to show the dispersion of a.
Types Absolute Relative measure Definition of Measures of Dispersion. Quartile Deviation gives the average amount by which the two quartiles differ from the median. What are the measure of dispersion explain with example.

Measures Of Dispersion In Statistics Definition Types

Measures Of Dispersion A Close View

Measures Of Dispersion Formulae And Examples What Is Dispersion With Examples Sample Size Youtube

Measures Of Dispersion Types Examples Applications Protonstalk
No comments for "Explain the Different Kinds of Measures of Dispersion"
Post a Comment